Syndrome Description
Learn more about M-CM
| Megalencephaly (enlarged brain) | 19 |
| Brain continuously enlarging over time | 14 |
| Hemimegalencephaly (enlarged brain with one side larger than the other) | 10 |
| Hemimegalencephaly progressing over time | 4 |
| Right side of brain larger than left | 7 |
| Left side of brain larger than right | 6 |
| Cerebral cortex abnormality | 6 |
| Dilated ventricles (ventriculomegaly) | 20 |
| Venous sinus thrombosis | 2 |
| Dilated venous sinuses | 3 |
| Obstructive hydrocephalus | 13 |
| Non-obstructive hydropcephalus | 7 |
| Thin corpus callosum | 2 |
| Thick corpus callosum | 8 |
| Enlarged cerebellum | 9 |
| Cerebellum growing progressively larger over time | 9 |
| Dilated perivascular spaces | 0 |
| Frontal lobe atrophy | 1 |
| Cerebral atrophy | 1 |
| Cerebellar tonsillar herniation (acquired protrusion of cerebellar tonsils through foramen magnum) | 16 |
| Ectopic cerebellar tonsils | 3 |
| Chiari I malformation (born with protrusion of cerebellar tonsils through foramen magnum) | 14 |
| Cavum vergae | 2 |
| Cavum septum pellucidum | 4 |
| Septum pellucidum cyst | 1 |
| Choroid plexus cyst(s) | 0 |
| Cystic abnormalities in white matter | 6 |
| Delayed myelination (absence of white matter) | 6 |
| White matter hyperintensities | 3 |
| Blood vessels extending through periventricular white matter | 0 |
| Heterotopic grey matter | 1 |
| Polymicrogyria (excessive amount of folds on the brain) | 11 |
| Pachygyria (thickening of folds of the brain) | 0 |
| Poor gyral formation | 1 |
| Macrogyric convolutions | 0 |
| Wide sylvian fissures | 0 |
| Blocked blood flow in brain | 0 |
| Gliosis | 2 |
| Cerebral calcifications | 0 |
| Optic nerve hydrops (accumulation of fluid around the optic nerve) | 0 |
| Thickened optic nerves | 1 |
| Prominent optic nerve | 0 |
| Optic nerve atrophy | 0 |
| Hydromyelia (dilation of the central canal of the spinal cord) | 0 |
| Syrinyx development (cyst on spinal cord) | 3 |
Other significant skin symptoms:
|
| Macrocephaly | 38 |
| Abnormal head shape | 23 |
| Prominent forehead (frontal bossing) | 31 |
| Small posterior fossa | 3 |
| Craniosynostosis (premature fusing of cranial sutures) | 2 |
| Increased intracranial pressure | 12 |
Other skull symptoms:
|
| Apnea | 14 |
| Difficulty controlling eye movements | 13 |
| Lethargy | 13 |
| Neck pain | 6 |
| Balance problems | 20 |
| Muscle weakness | 26 |
| Numbness | 1 |
| Tingling in arms or legs | 1 |
| Clonus | 5 |
| Vision problems | 11 |
| Difficulty swallowing | 11 |
| Ringing or buzzing in the ears | 4 |
| Hearing loss | 0 |
| Vomiting | 6 |
| Insomnia | 6 |
| Changes in fine motor skills | 8 |
| Depression | 1 |
Other brainstem abnormalities:
|
| Yes | 11 |
| No | 30 |
| Unsure | 0 |
Results:
|
| Hypotonia (low muscle tone) | 35 |
| Hypertonia (high muscle tone) | 1 |
| Hypotonia resolved after time | 4 |
Other muscle symptoms:
|
|
| Seizures | 15 |
| Headache | 6 |
| Lethargy | 11 |
| Ischemic attacks or strokes | 0 |
| Thromboembolic events | 0 |
| Facial Nerve Palsy | 2 |
| Hemiplegia (paralysis on one side of the body) | 0 |
| Cerebral palsy | 2 |
| Regression/loss of skills | 6 |
| Poor coordination | 16 |
| Dizzy spells | 1 |
| Trouble sleeping | 9 |
| Change in appetite | 3 |
| Fatigue | 7 |
Other:
|
Learn more about M-CM
Order brochures or download a PDF
Guidelines from published research literature
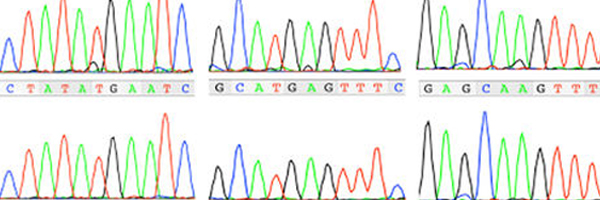
Guidance for clinical genetic testing

Explore the research literature related to M-CM

An extensive list of resources